Understanding a Tooth That Can't Be Saved
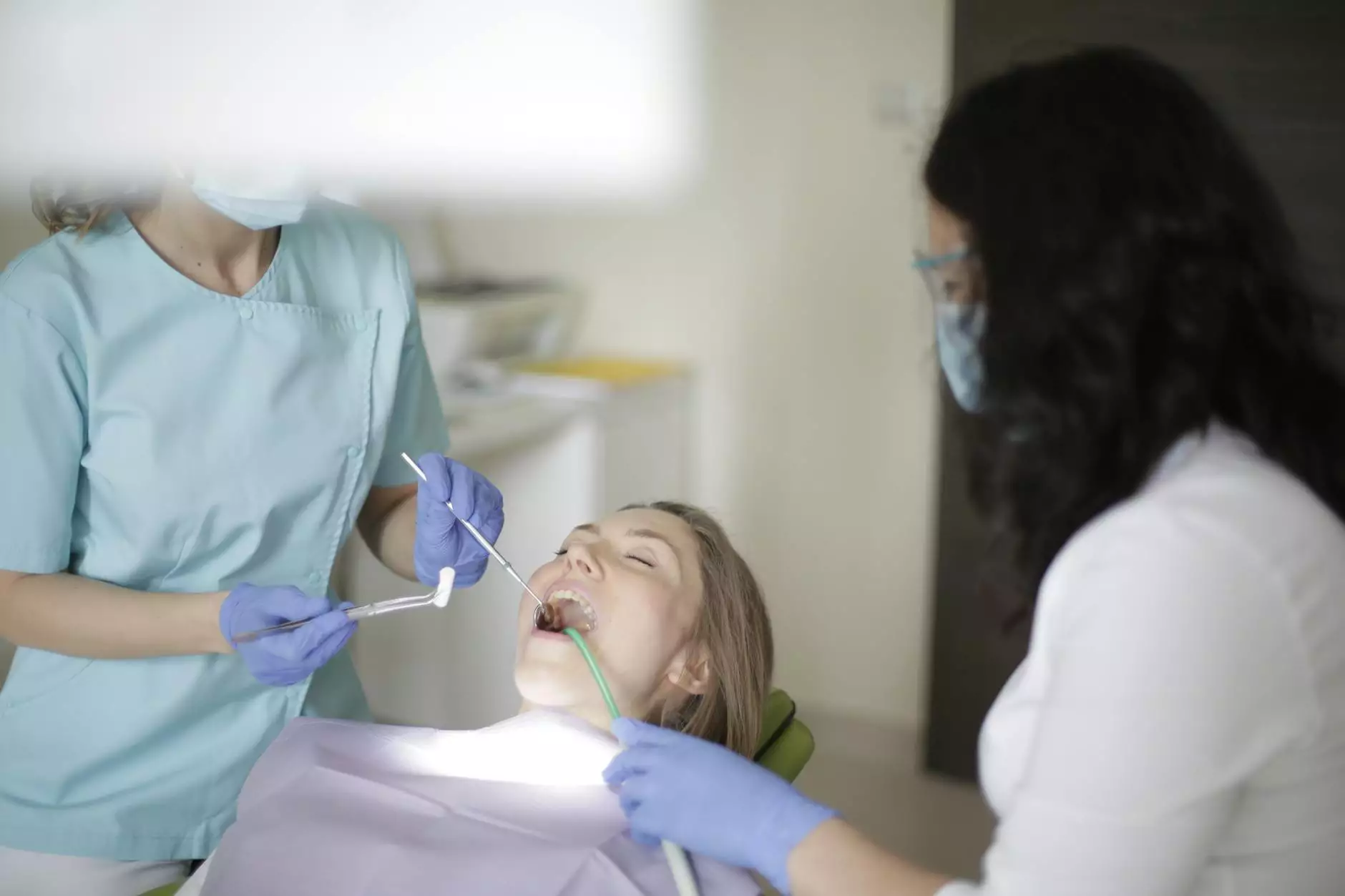

When it comes to dental health, many patients face difficult decisions, especially regarding a tooth that can't be saved. It's crucial for patients to understand not only what leads to this situation but also the subsequent steps and treatment options available. This article delves deeply into the factors contributing to tooth loss, how to prevent it, and the best practices in dental care.
1. Causes of Tooth Loss
The journey to losing a tooth may stem from various factors. Identifying these causes is essential for maintaining overall dental health. Here are the most common reasons a tooth that can't be saved occurs:
- Severe Tooth Decay: The most prevalent cause is tooth decay that has progressed to an irreparable stage. Regular dental check-ups help in identifying cavities early, preventing this situation.
- Gum Disease: This condition can lead to the deterioration of the supporting structures of teeth. Periodontitis, a more advanced stage, often results in tooth mobility and potential loss.
- Trauma or Injury: Accidents or injuries that result in a fractured tooth or root can sometimes render a tooth irreparable.
- Advanced Age: As we age, our enamel wears down, making teeth more susceptible to decay and fractures.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people are more prone to certain dental issues due to family history, which can impact the health of their teeth and gums.
2. Recognizing the Signs of Irreparable Damage
Understanding when a tooth may not be savable is critical for effective dental care. Here are some signs to watch for:
- Persistent Pain: Continuous pain in a tooth, even after treatment, may indicate serious damage or infection.
- Visible Decay: If extensive decay is visible, it could suggest the tooth has deteriorated beyond saving.
- Gum Swelling: Swollen gums around a tooth may suggest underlying issues, including infection that could lead to tooth loss.
- Mobility: A tooth that feels loose might indicate severe periodontal disease.
3. Dental Assessment and Diagnosis
If you suspect you have a tooth that can't be saved, it's essential to consult with a professional dentist. The assessment generally includes:
- Comprehensive Examination: Your dentist will visually examine your teeth and gums for any signs of issues.
- X-rays: These are vital for assessing the extent of damage, particularly to the roots of the tooth and surrounding bone structure.
- Pulp Vitality Test: This test determines if the pulp in the tooth is still healthy or affected by decay/infection.
4. Options for a Tooth That Can't Be Saved
When a tooth is deemed irreparable, several treatment alternatives are available. Understanding these options can help you make informed decisions:
- Extraction: The most straightforward solution is to extract the tooth to prevent pain and further health issues.
- Replacement Options: Following extraction, several options such as dental implants, bridges, or partial dentures can restore functionality and aesthetics.
- Bone Grafting: If a dental implant is planned, bone grafting may be necessary to ensure there is adequate bone structure to support the implant.
5. Preventive Measures for Maintaining Dental Health
Preventing a scenario where a tooth that can't be saved becomes a reality is achievable through diligent oral hygiene and lifestyle choices. Here are the most effective measures:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule dental visits every six months to allow for early detection of issues.
- Proper Oral Hygiene Practices: Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to maintain gum and tooth health.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports oral health. Limit sugary snacks and beverages that contribute to decay.
- Fluoride Treatments: Ask your dentist about professional fluoride treatments to strengthen enamel and prevent decay.
6. The Emotional Impact of Losing a Tooth
The loss of a tooth can have emotional and psychological effects on individuals.
Understandably, many people experience feelings of:
- Embarrassment: Worrying about appearance can be distressing, prompting many to avoid social situations.
- Loss of Confidence: Missing teeth can affect one's self-esteem, making everyday interactions challenging.
- Anxiety: Prospective dental procedures can lead to anxiety, especially if previous experiences were painful or discomforting.
7. Consult Your Dentist: The Importance of Professional Guidance
It’s important to seek professional guidance from your dentist at Grosso Family Dentistry. They can provide personalized care tailored to your dental needs. Here’s why consulting a dental professional is crucial:
- Expert Evaluation: Dentists are trained to identify the health of your teeth and gums and provide appropriate recommendations.
- Access to Advanced Treatments: Modern dental offices offer a range of treatments, allowing you to select what best fits your situation.
- Supportive Care: Professionals can also address your emotional and psychological concerns about losing a tooth.
8. Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Dental Health
Understanding the implications of having a tooth that can't be saved is the first step toward making informed decisions about your dental health. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take an active role in preserving your smile. Furthermore, maintaining an ongoing relationship with dental professionals, such as those at Grosso Family Dentistry, ensures that you receive the best care possible to keep your teeth healthy for a lifetime.
9. About Grosso Family Dentistry
At Grosso Family Dentistry, we prioritize the health and happiness of our patients. Our experienced team specializes in General Dentistry, Cosmetic Dentistry, and Dentists committed to offering comprehensive care and support. If you have concerns about a tooth that can't be saved or just wish to optimize your dental health, don’t hesitate to reach out. Your smile is our passion.
tooth that can t be saved